India's Agriculture contribution to GDP and world
The agricultural sector in India is a verdant realm, brimming with a plethora of crops that nourish not just the nation's populace but also the world. The sector, which employs a vast majority of the country's population, is a vital contributor to the Indian economy. India is a major player in the global food production landscape, with rice, wheat, sugarcane, cotton, and a wide array of fruits and vegetables among the crops that it cultivates with exceptional finesse. In addition, the country is a significant producer of milk, poultry, and fish, making it a true agricultural powerhouse. Despite the challenges of limited land and water resources, the Indian agricultural sector continues to flourish, adapting to the ever-evolving demands of feeding a nation of over 1.3 billion people.
The bountiful harvest of India's agricultural sector, a vital contributor to the nation's sustenance and global food production.
Indian agriculture history
The rich tapestry of Indian agricultural history is woven with threads of ancient wisdom and modern innovation. The practice of farming in the country dates back to the Indus Valley Civilization around 3300 BCE, where a diverse array of crops such as wheat, barley, peas and sesame were meticulously tended to. The ancient Indian text, "Arthashastra," written around 300 BCE, provides a glimpse into the sophisticated agricultural practices that existed during that time, including irrigation, crop rotation, and the use of manures and fertilizers.
Fast forward to the medieval period, the Indian agricultural system was based on the traditional three-field system, where one-third of the land was left fallow, one-third was used for growing a non-irrigated crop, and one-third was used for growing an irrigated crop. This system was widely used in the northern and northwestern regions of India.
The arrival of the British during the colonial period brought about a new chapter in Indian agricultural history. They introduced new crops such as tea, coffee, rubber, and opium, and also implemented new agricultural practices such as the use of modern tools and machinery.
In more recent times, Indian agriculture has undergone a metamorphosis, embracing advanced technology and scientific methods to enhance crop yields and productivity. Despite these advancements, Indian agriculture still faces challenges such as low productivity, lack of access to markets, and climate change. The government of India has implemented various schemes and policies to address these issues and to promote sustainable agriculture in the country. As we look to the future, Indian agriculture is poised to continue its legacy of cultivating not just crops, but also a rich and diverse agricultural heritage.
The fertile soil of India's agricultural history, teeming with tales of ancient wisdom and modern progress.
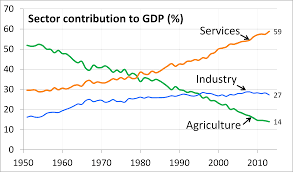
Current situation of agriculture sector in India
The agricultural sector in India is currently navigating through a sea of challenges, but it is not without its own set of opportunities. Despite low productivity caused by the use of outdated methods, lack of access to modern technology and training, the sector holds an immense potential for growth. The lack of access to markets for farmers, making it difficult for them to sell their products at fair prices is a major issue, but it also presents an opportunity to create new market linkages and better price discovery mechanisms. Climate change, with its extreme weather events such as droughts and floods, is affecting agriculture, but it also presents an opportunity to innovate and adapt to these changes.
The Indian government has taken steps to address these challenges by implementing policies and schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana which provides crop insurance for farmers and the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana, which focuses on improving irrigation infrastructure. The National Agriculture Market (e-NAM) was launched to link farmers with buyers and to improve the price discovery mechanism for farm products. These steps are helping to pave the way for a more resilient and sustainable agricultural sector in India.
Despite the challenges, Indian agriculture sector has a great potential to grow and provide livelihoods to a large portion of the population. With the right policies, investments and support, the sector can overcome the current challenges and create a brighter future for farmers and the nation.
The agricultural sector in India, a verdant landscape of challenges and opportunities, ripe for growth and prosperity.
Farmer's Condition in India
The condition of farmers in India is a multifaceted reality, shaped by a plethora of factors that both impede and empower. Many farmers in India struggle with low productivity, small and fragmented landholdings, inadequate irrigation, and lack of access to credit and markets. These issues make it difficult for them to earn a livelihood and provide for their families.
A significant challenge faced by Indian farmers is the price volatility and lack of fair prices for their hard-earned produce. Many farmers are forced to sell their products at low prices to intermediaries, who then sell them at a higher price to consumers. This lack of access to fair prices can make it difficult for farmers to earn a profit and can lead to financial insecurity.
Climate change is also a formidable force that affects farmers in India, with extreme weather events such as droughts and floods becoming more frequent. This can lead to crop failures and financial losses for farmers.
Despite these challenges, many farmers in India continue to work hard and to provide food for the country's large population. The government of India has implemented various policies and schemes to support farmers and to improve their livelihoods, such as the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana, which provides crop insurance for farmers, and the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana, which focuses on improving irrigation infrastructure. However, more needs to be done to ensure that the hardworking farmers in India get their fair share of support and livelihood opportunities.
The condition of India's farmers, a delicate balance of struggles and perseverance, in need of support and recognition.
What can improve agricultural sector?
The agricultural sector in India is a vital cog in the wheel of the nation's economy and food security, and there are several ways to enhance its productivity and resilience.
- Boosting productivity: By equipping farmers with modern technology, training and scientific methods, they can tap into the full potential of their land and increase their yields.
- Access to fair markets: By creating a national market for agricultural products, and connecting farmers to buyers through technology, farmers can access fair prices for their products.
- Irrigation infrastructure: Building dams, canals, and other irrigation infrastructure can help farmers cultivate crops in dry and arid regions, reducing dependency on monsoon.
- Credit and financial services: Providing farmers with access to credit and financial services can enable them to invest in modern tools and equipment, and improve their livelihoods.
- Crop insurance: Offering crop insurance can help mitigate the impact of crop failures caused by extreme weather events and natural disasters.
- Research and Development: Investing in research and development can lead to the discovery of new techniques and technologies that can improve crop yields and reduce the impact of climate change.
- Extension services: By providing extension services to farmers, they can be informed about the latest scientific methods, technologies, market information and government schemes.
- Land reforms: By redistributing land to small and marginal farmers and providing them with better access to resources and services, the government can help to improve their livelihoods and increase agricultural productivity.
In conclusion, by embracing these solutions and taking a holistic approach, India can unlock the full potential of its agricultural sector, empower farmers, and secure food for its people.
Unlocking the full potential of India's agricultural sector, a key to empower farmers and secure the nation's food security.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the situation of farmers in India can be improved by a multifaceted approach that addresses the various challenges they face. This includes implementing policies and programs that increase productivity through modern technology and training, providing access to fair markets through better market linkages and price discovery mechanisms, investing in irrigation infrastructure, providing access to credit and financial services, crop insurance, extension services and land reforms. By addressing these issues, the government can empower farmers, improve their livelihoods, and secure food for the nation. A comprehensive and holistic approach is essential to uplift the agricultural sector and the farmers of India.
You might be also interest in -





.jpeg)





.jpeg)


0 Comments
Let me know if you have any doubts.
and follow us.